Induction heating for surface triggering styrene polymerization
2013/5/16 Views
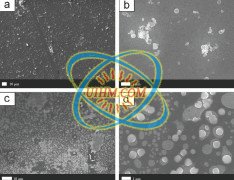 Titanium and its alloys present high interests for technological applications due to their high resistance corrosion, mechanical properties and biocompatibility [1-5]. For example, titanium is largely used as orthopedic metallic implant [6]. In addition, TiO2 layers on Ti possess a wide variety of functional properties in self-cleaning [7,8], photocatalysis [9], gas sensing [10,11], solar energy conversion [12] and wettability [13].
Titanium and its alloys present high interests for technological applications due to their high resistance corrosion, mechanical properties and biocompatibility [1-5]. For example, titanium is largely used as orthopedic metallic implant [6]. In addition, TiO2 layers on Ti possess a wide variety of functional properties in self-cleaning [7,8], photocatalysis [9], gas sensing [10,11], solar energy conversion [12] and wettability [13].In combination with those remarkable characteristics, some Ti applications require specific surface properties that can be imparted with suitable surface functionalizations of the TiO2 oxide layer. Creating a thin and adherent polymeric layer is one of the common ways to achieve such a surface modification. This kind of polymeric layers can be obtained via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). Nowadays, a wide variety of materials have been reported as suitable substrates for sur-face-initiated ATRP: glass, metals, metal oxides, etc. [14-20]. ATRP takes place through a reversible redox reaction involving a transition metal catalyst which is oxidized as the polymer is converted from the dormant state to the radical active state. The mechanism involves the transfer of a halogen atom from an initiator to the metal catalyst yielding an active radical initiator, which can then lead to the monomer polymerization.
Down Attachment
- DownloadAttach1: Induction heating for surface triggering styrene polymerization.pdf Clicks
Good
Bad






Newest Comment
No Comment
Post Comment